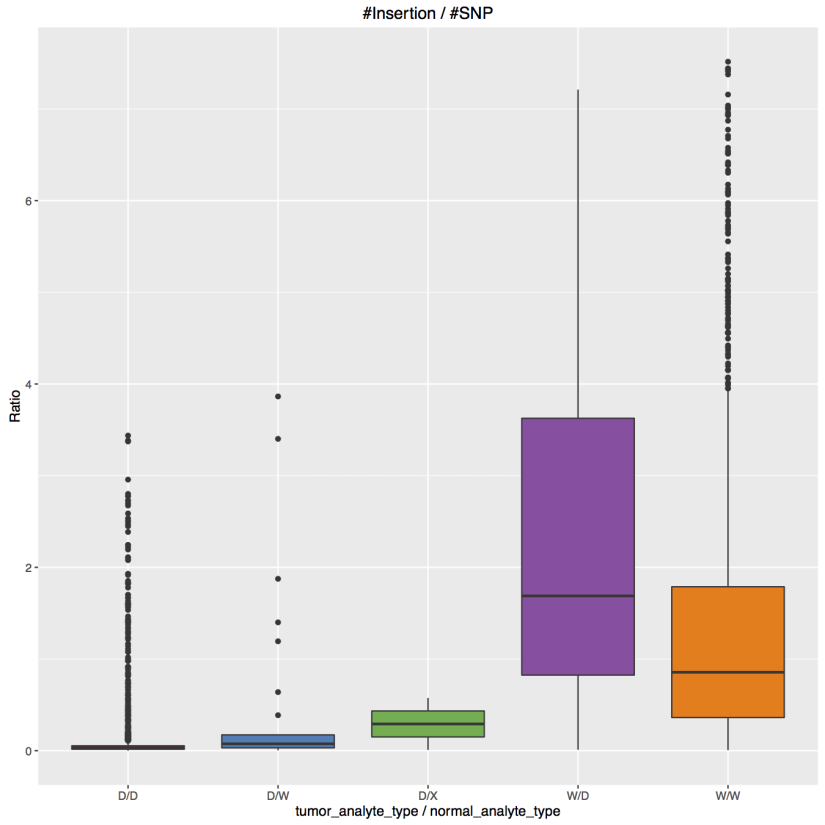
We observed excess numbers of insertions and deletions called by MuTect2 in some tumor-normal pairs, especially those tumor samples that have undergone whole genome amplification (WGA).
The WGA status can be found in the analyte_type property within analyte and aliquot. (For an individual case, analyte information can be viewed in the Portal by expanding items in the Biospecimen frame. See this example.) TCGA analyte type can be also identified in the 20th character of TCGA barcode, with possible values of “D”, “W” or “X”. "D" is sample DNA, "W" and "X" correspond to WGA.
The figure above is a boxplot of ratio, defined by number of insertions vs. number of single nucleotide variants called by MuTect2, and categorized by 5 different combinations of normal/tumor analyte type. It is very clear that WGA tumor samples result in relatively more insertions.
Detailed inspection of read pileup suggests many of such insertions are mainly supported by soft-clipped bases, and are likely to be false-positive artifacts. It has been known that artificial chimera reads could form during the Multiple Displacement Amplification reaction[1], such as the one used to generate the WGA libraries by REPLI-g.
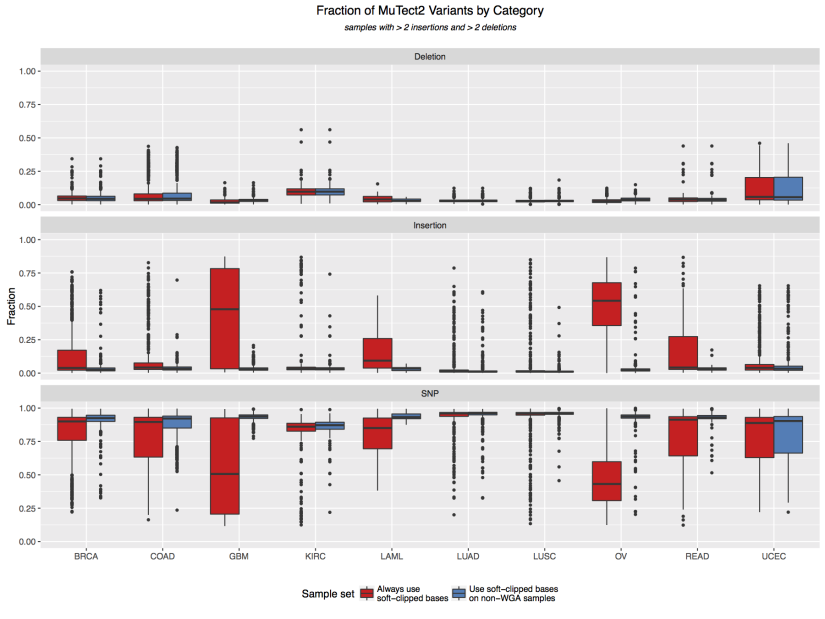
In order to increase specificity, we re-analyzed all tumor WGA samples with MuTect2 option –dontUseSoftClippedBases. This process affected 1503 tumor normal pairs in 10 TCGA projects, namely BRCA, COAD, GBM, KIRC, LAML, LUAD, LUSC, OV, READ, and UCEC. A boxplot comparison of fractions of different variant categories is shown below, with red color denoting the original MuTect2 calls, and blue color denoting results from our WGA sample re-analysis. The re-analysis significantly reduce the relative proportion of insertions in most of the WGA samples, and this new dataset replaced the existing data on GDC data portal during the Oct 2016 release. This pipeline modification has likely removed some true positive insertions in VCFs derived from WGA samples.
In addition to WGA samples, we have also seen insertions supported purely by soft-clipped bases in some sporadic tumor samples, although in a much smaller scale. We suggest users to consume these INDEL calls with extra care.
Addendum June 30, 2017: We would like to clarify that the effects on variant calls originating from aliquots that underwent WGA are not necessarily an artifact of Mutect2. Out of the four GDC variant calling pipelines, the one that uses Mutect2 is the only one that calls indels. WGA artifacts are most apparent when observing indel variants, so Mutect2 is the only pipeline that could be meaningfully discussed in this context.
[1] 2006. Zhang, K., Martiny, A.C., et al. Sequencing genomes from single cells by polymerase cloning. Nature Biotechnology 24:680-686.
(Created on: September 15, 2016 • Last updated on: June 11, 2017)